Custom Exception, Spring Boot는 예외 처리를 어떻게 하는가
📌 Before
1
2
3
4
5
public UserResponse getUser(Long userId) {
return userRepository.findById(userId)
.map(user -> UserResponse.of(user.getEmail(), user.getNickname()))
.orElseThrow(() -> new IllegalArgumentException("해당 사용자를 찾을 수 없습니다."));
}
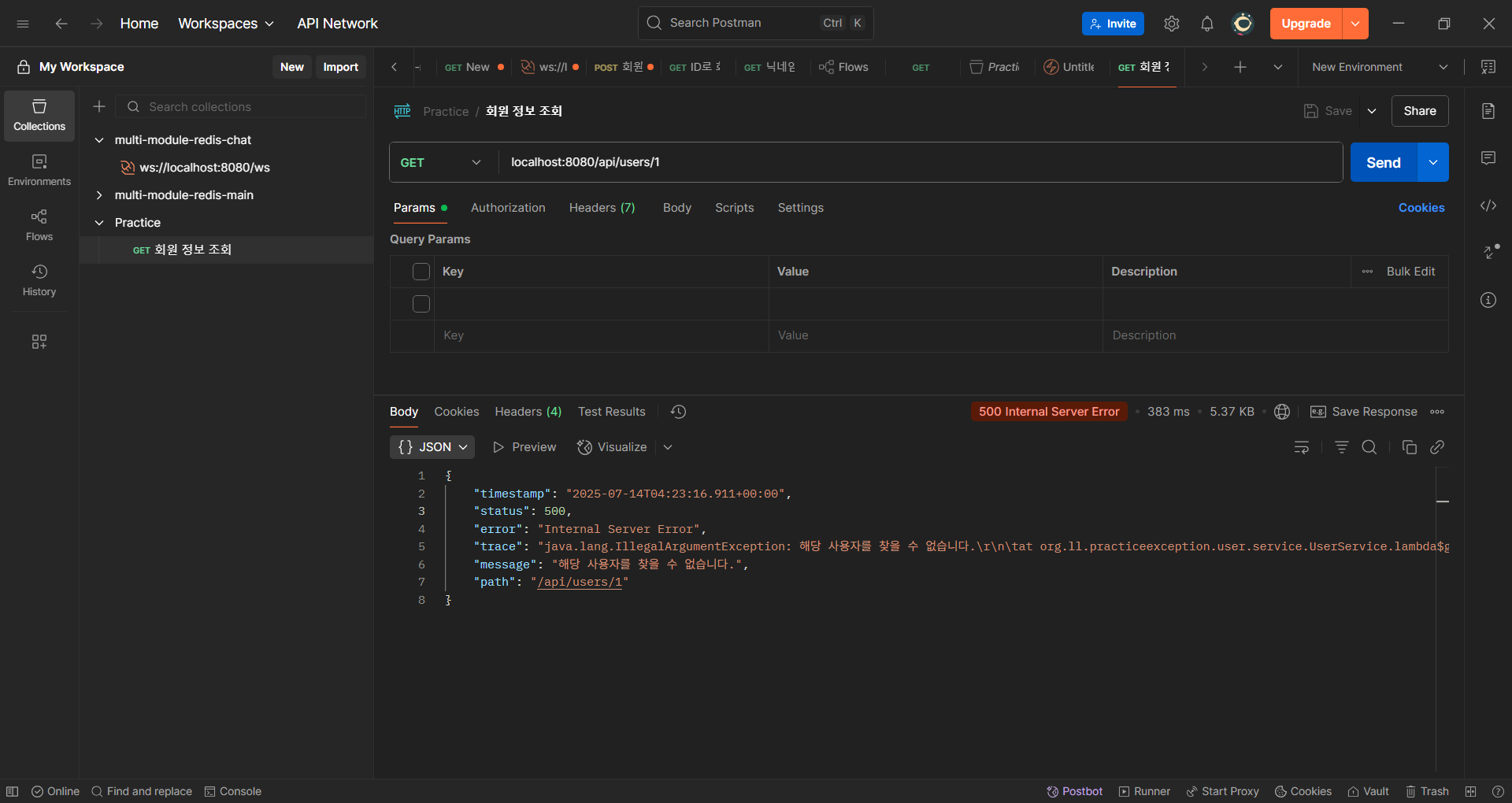
간단한 회원 조회 로직이다. 올바른 회원 정보를 찾지 못하면 IllegalArgumentException 을 컨트롤러에 던지게 된다. 이러한 예외 처리의 한계는 무엇일까?
먼저 IllegalArgumentException 을 직역하면 잘못된 인자에 대한 예외인데, 파라미터로 주어진 userId 는 올바른 형식일 수도 있다. 단지 DB에 해당 사용자가 존재하지 않을 뿐이다.
또한 별도의 handler가 없다면 IllegalArgumentException 은 항상 같은 오류 코드를 가지게 된다. 실제로는 IllegalArgumentException 로 처리된 예외 중에서 어떤 예외는 400, 어떤 예외는 404로 처리해야 하는 경우가 있을 수 있다.
따라서 세밀한 예외 제어와 명확한 의미 전달을 위해 예외 처리를 커스텀한다.
📌 ErrorCode
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
@Getter
@AllArgsConstructor
public enum ErrorCode {
// 404
USER_NOT_FOUND(HttpStatus.NOT_FOUND.value(), "사용자가 존재하지 않습니다."),
// 400
INVALID_INPUT(HttpStatus.BAD_REQUEST.value(), "잘못된 입력입니다."),
// 500
NOT_DEFINED(HttpStatus.INTERNAL_SERVER_ERROR.value(), "정의되지 않은 에러입니다.")
;
private final int code;
private final String message;
}
먼저 enum 상수를 정의한다. code 는 예외와 관련된 HTTP 상태 코드, message 는 예외에 대한 설명이다.
📌 CustomException
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
@Getter
public class CustomException extends RuntimeException {
private final int code;
private final String message;
public CustomException(ErrorCode errorCode) {
this.code = errorCode.getCode();
this.message = errorCode.getMessage();
}
public CustomException(ErrorCode errorCode, String detail) {
this.code = errorCode.getCode();
this.message = errorCode.getMessage() + " : " + detail;
}
}
CustomException 는 모든 예외가 동일한 형태를 가지도록 표준화한다. 다시 말해 모든 예외가 code 와 message 를 가지도록 강제한다.
RuntimeException 을 상속하고 있는데, 이를 통해 별다른 throws 또는 try-catch 선언 없이 예외가 자동으로 상위 계층으로 전파된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
// 서비스
public UserResponse getUser(Long userId) {
return userRepository.findById(userId)
.map(user -> UserResponse.of(user.getEmail(), user.getNickname()))
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.USER_NOT_FOUND));
}
// 컨트롤러
@GetMapping("/users/{userId}")
public UserResponse getUser(@PathVariable Long userId) {
return userService.getUser(userId);
}
RuntimeException 을 상속하면 위 코드와 같이 throws 선언이 필요하지 않으며 컨트롤러에서도 try-catch 문이 필요하지 않다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
15
16
17
// 서비스
public UserResponse getUser(Long userId) throws CustomException {
return userRepository.findById(userId)
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.USER_NOT_FOUND));
}
// 컨트롤러
@GetMapping("/users/{userId}")
public UserResponse getUser(@PathVariable Long userId) {
try {
return userService.getUser(userId);
} catch (CustomException e) {
// ..
throw e;
}
}
그러나 RuntimeException 이 아니라 Exception 을 상속했다면 위 코드와 같이 작성해야 한다.
📌 CustomExceptionHandler
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
@ControllerAdvice
public class CustomExceptionHandler {
@ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class)
protected ResponseEntity<ErrorResponse> handleCustomException(CustomException ex) {
ErrorResponse errorResponse = new ErrorResponse(ex);
return ResponseEntity
.status(ex.getCode())
.body(errorResponse);
}
// ...
}
CustomExceptionHandler 는 발생한 예외를 중앙집중식으로 처리하는 핸들러이다.
@ControllerAdvice 는 모든 컨트롤러에서 발생하는 예외를 가로채서 처리할 수 있도록 하는 어노테이션이다.
@ExceptionHandler 는 특정 타입의 예외 발생을 감지하고, 해당 메서드가 호출되도록 하는 어노테이션이다.
CustomException 이 RuntimeException 을 상속하도록 구현하였기 때문에 예외가 발생하면 자동으로 CustomExceptionHandler 까지 전파된다.
📌 예외 처리 흐름
1
2
3
4
5
public UserResponse getUser(Long userId) {
return userRepository.findById(userId)
.map(user -> UserResponse.of(user.getEmail(), user.getNickname()))
.orElseThrow(() -> new CustomException(ErrorCode.USER_NOT_FOUND));
}
예외가 발생하면 CustomException 이 생성되어 생성자를 호출한다. 이후 예외는 컨트롤러로 전파된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
@GetMapping("/{user-id}")
public ResponseEntity<UserResponse> getUser(
@PathVariable("user-id") Long userId
) {
UserResponse userResponse = userService.getUser(userId);
return ResponseEntity.ok(userResponse);
}
컨트롤러에 별도의 예외 처리 구문이 없으므로 계속 상위로 전파된다. CustomException 은 DispatcherServlet 까지 올라가며, 이 시점에서 메서드 실행은 중단된다.
DispatcherServlet 은 CustomException 을 수신하고 HandlerExceptionResolver 체인을 호출하여 예외 처리기에 예외 처리를 위임한다.
가장 먼저 ExceptionHandlerExceptionResolver 가 호출되어 ExceptionHandler 어노테이션이 붙은 메서드를 실행한다. 먼저 컨트롤러에서 @ExceptionHandler(CustomException.class) 를 찾고, 이후 전역 예외 처리기인 @ControllerAdvice 에서 해당 예외를 처리할 핸들러를 찾는다.
다음으로 ResponseStatusExceptionResolver 가 호출된다. 예외 관련 클래스에 @ResponseStatus 가 있는지 확인한다. 위 예제에서 CustomException 에는 해당 어노테이션이 없으므로 넘어간다.
마지막으로 DefaultHandlerExceptionResolver 가 호출된다. Spring 내부의 기본적인 예외를 처리하며, CustomException 은 Spring 기본 예외가 아니므로 넘어간다.
각 리졸버가 순차적으로 실행되는 것이 아니라, 한 리졸버가 호출되면 나머지 리졸버는 호출되지 않는다.
위 예제에서 CustomExceptionHandler 에 @ControllerAdvice 어노테이션이 붙어있으므로, 해당 핸들러에서 적절한 예외 처리 메서드 handleCustomException 을 실행한다. 최종적으로 CustomExceptionHandler 가 리턴한 ResponseEntity 가 클라이언트에게 전달된다.
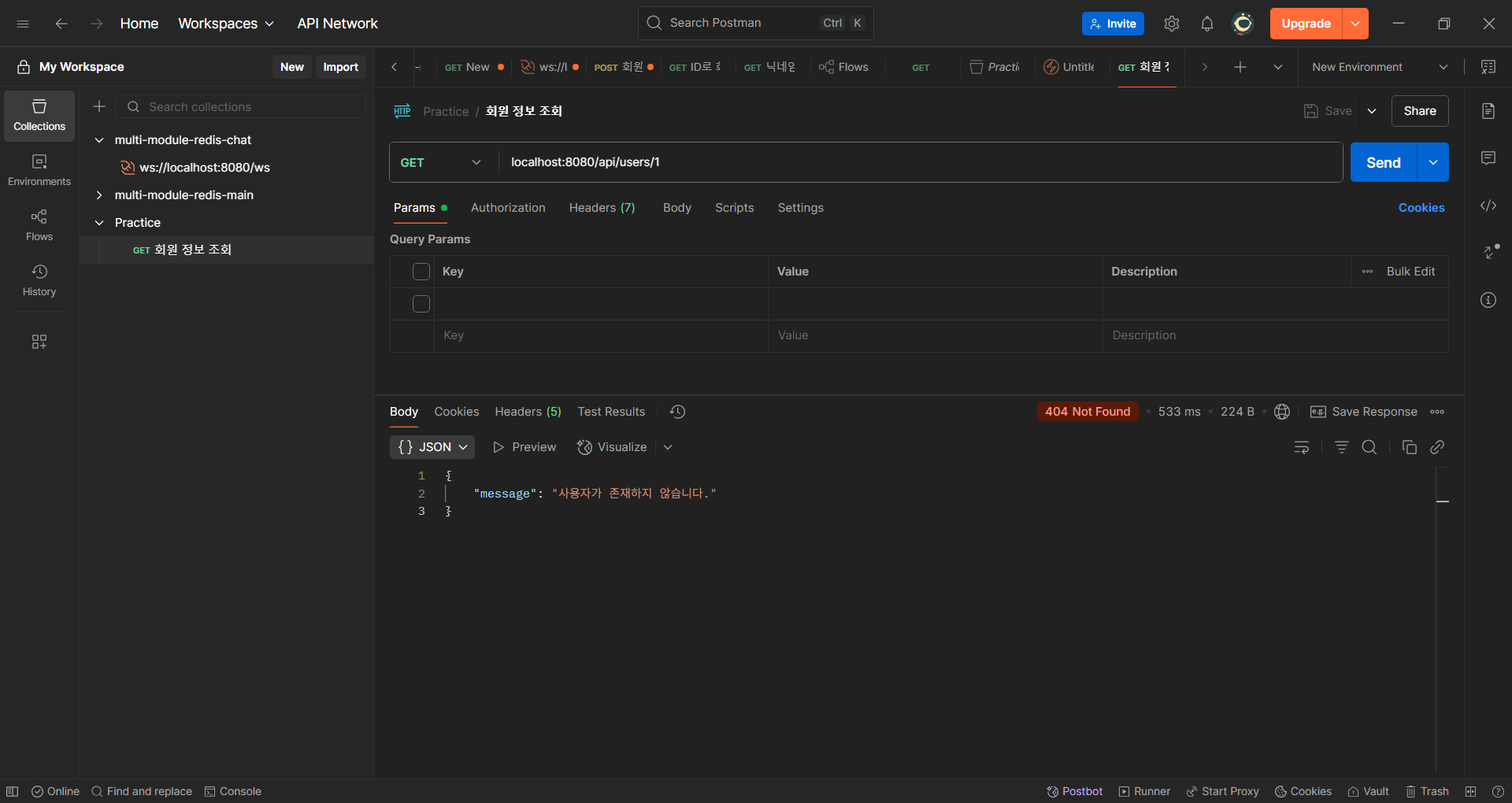
📌 After
예외에 대해 적절한 상태 코드가 설정되었다. 👍
📌 깃허브
https://github.com/whqtker/practice-custom-exception